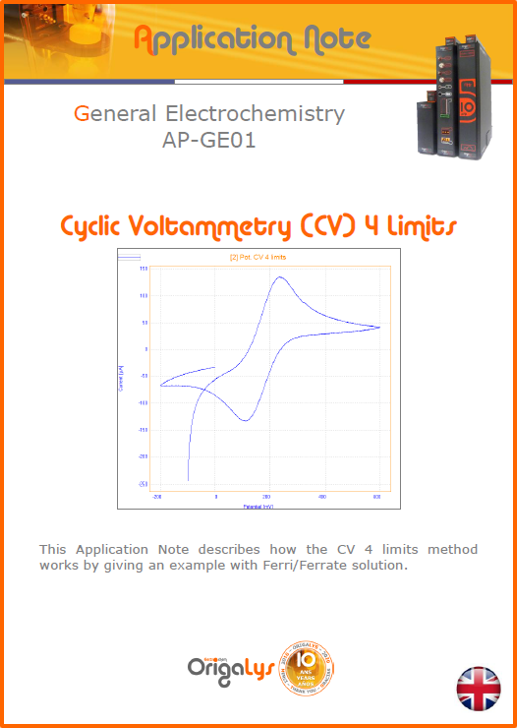
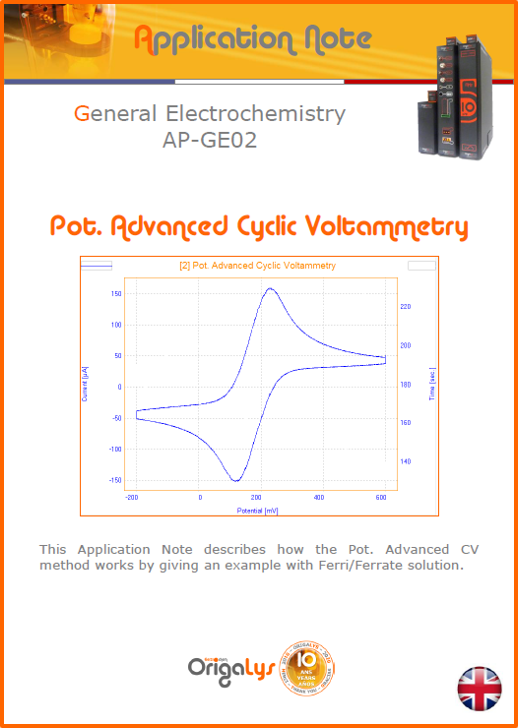
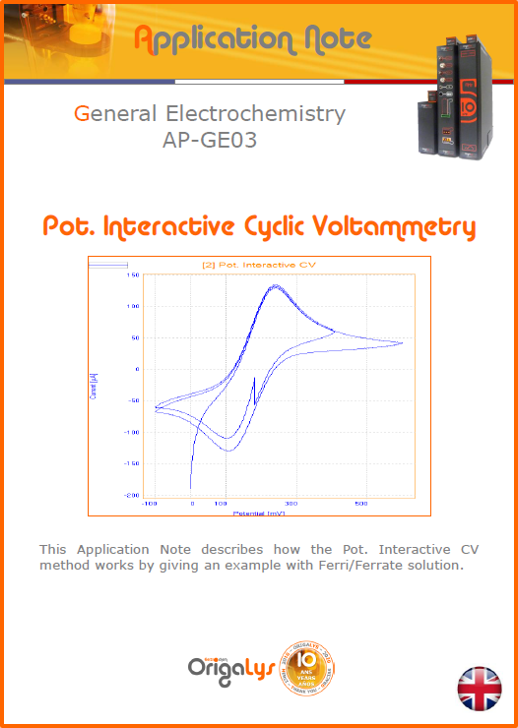
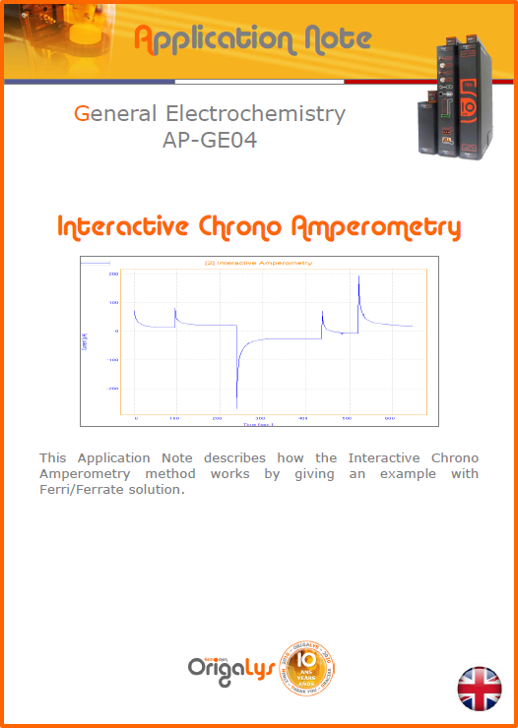
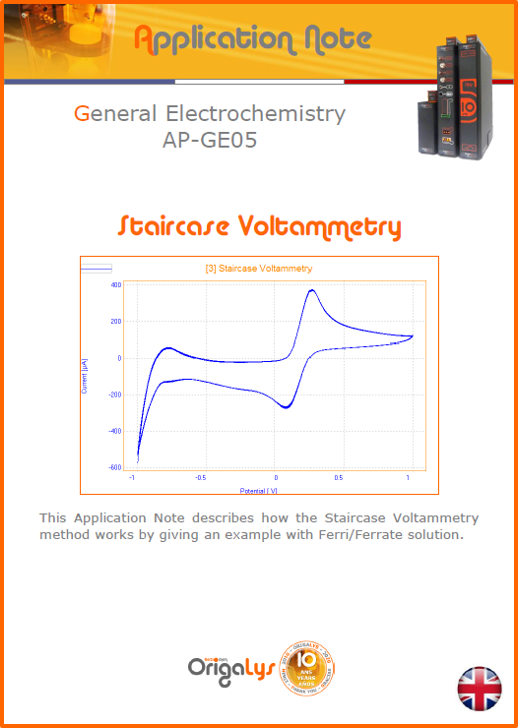
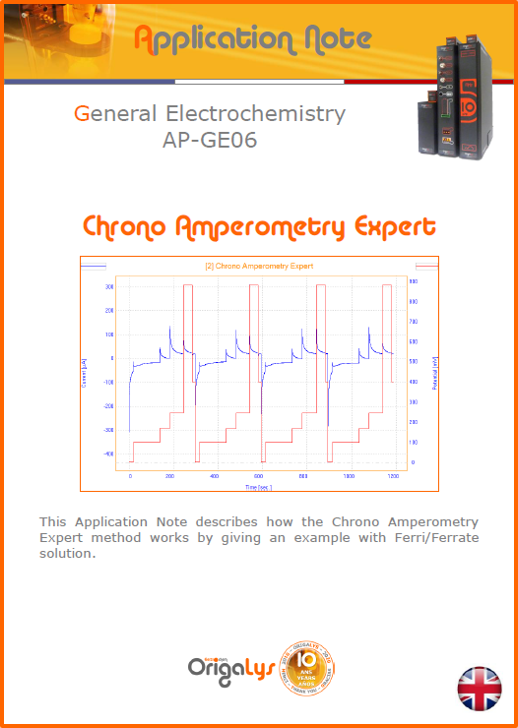
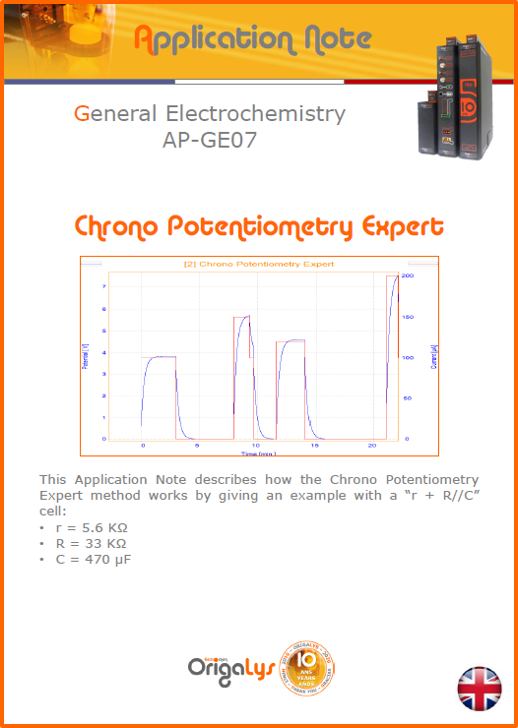
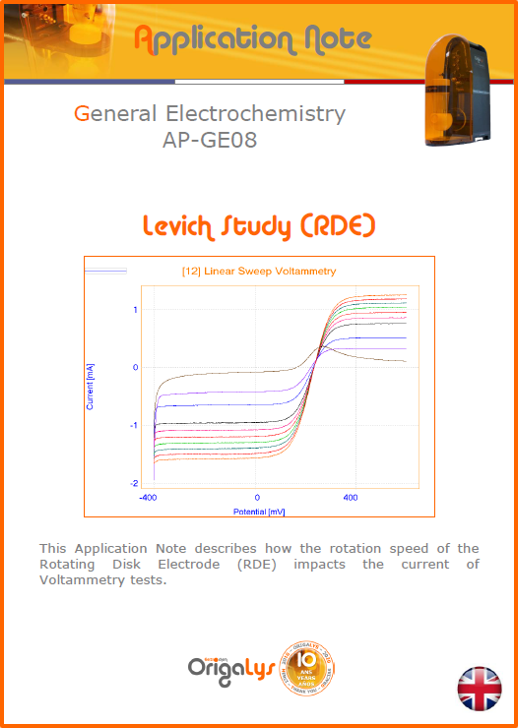
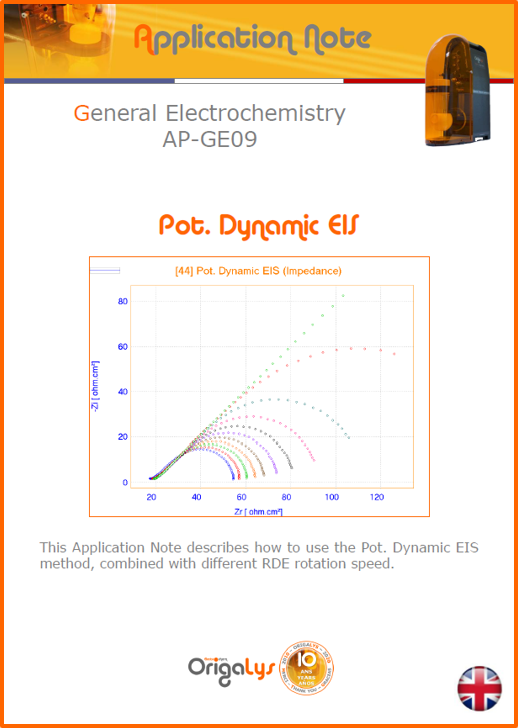
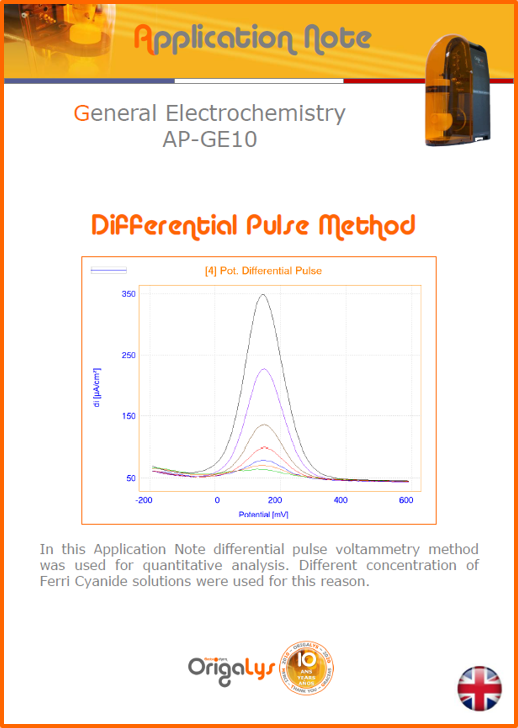
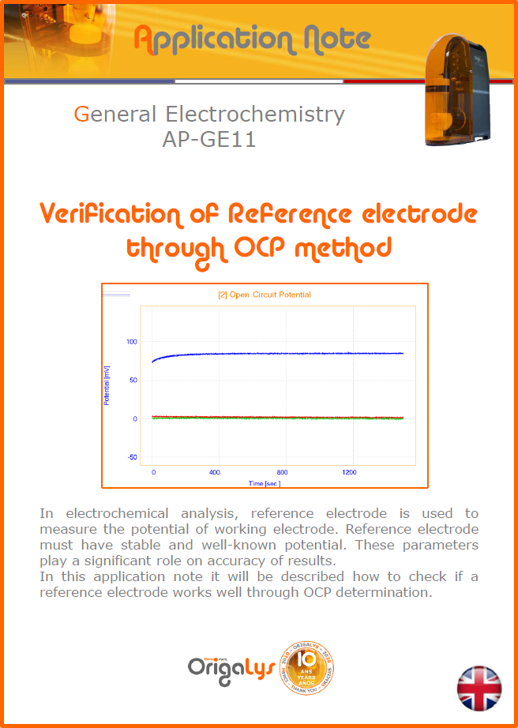
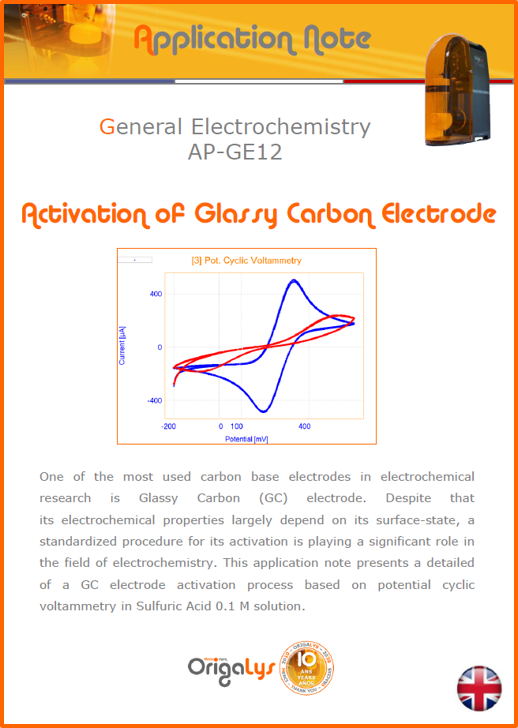
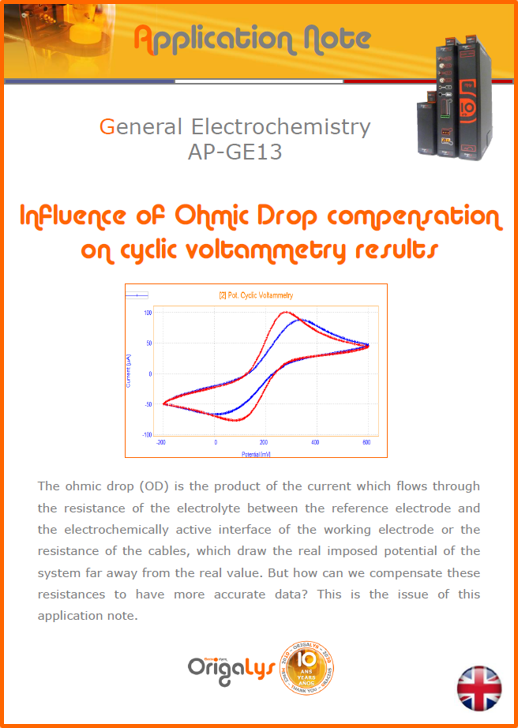
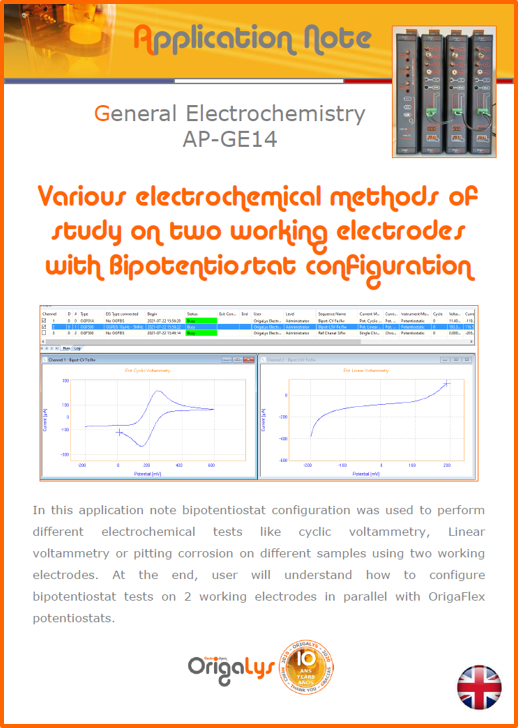
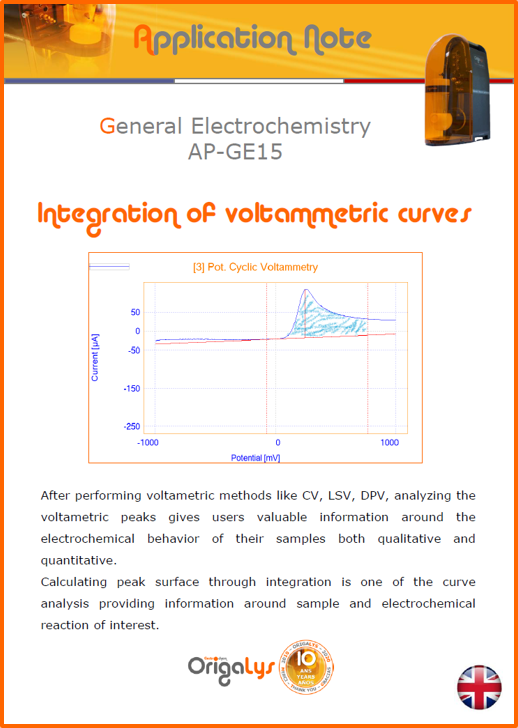
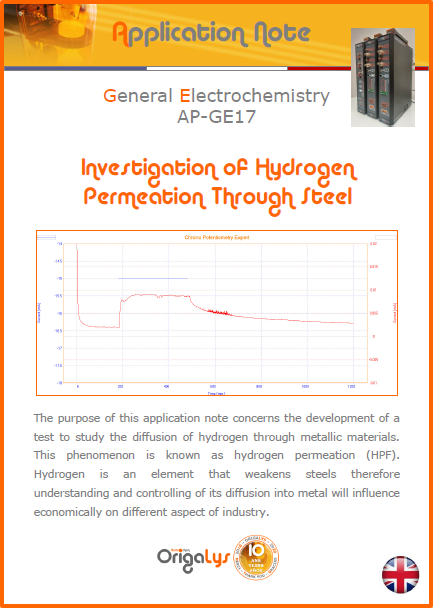
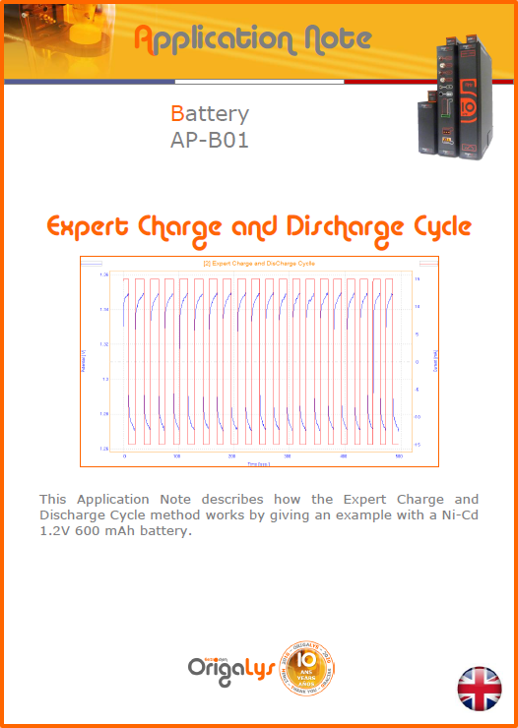
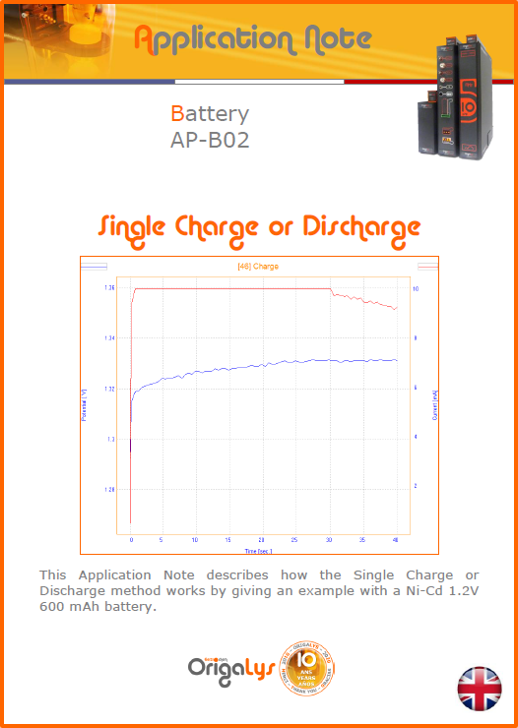
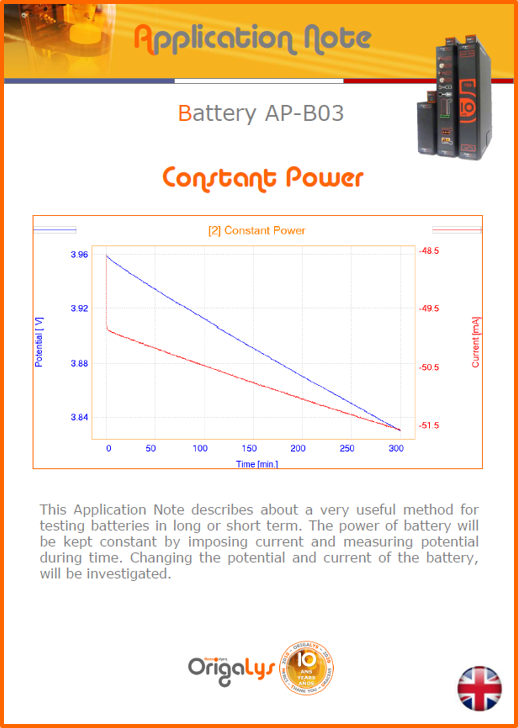
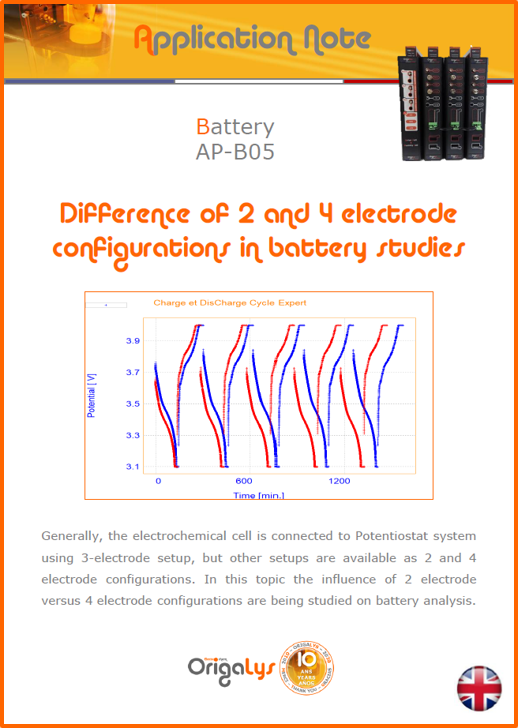
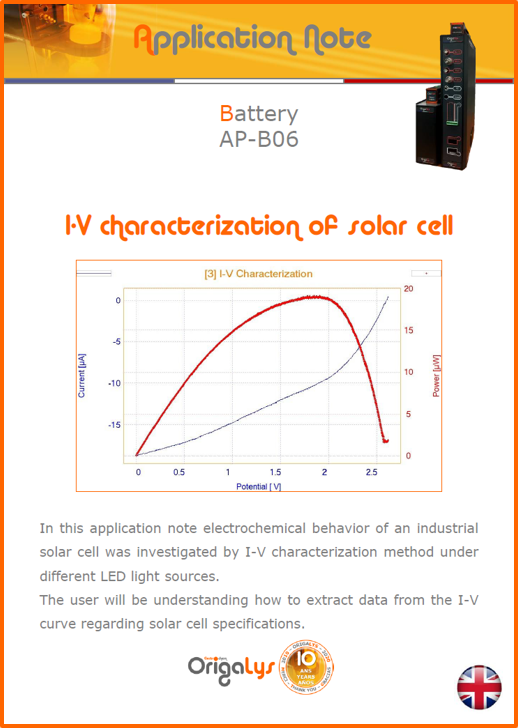
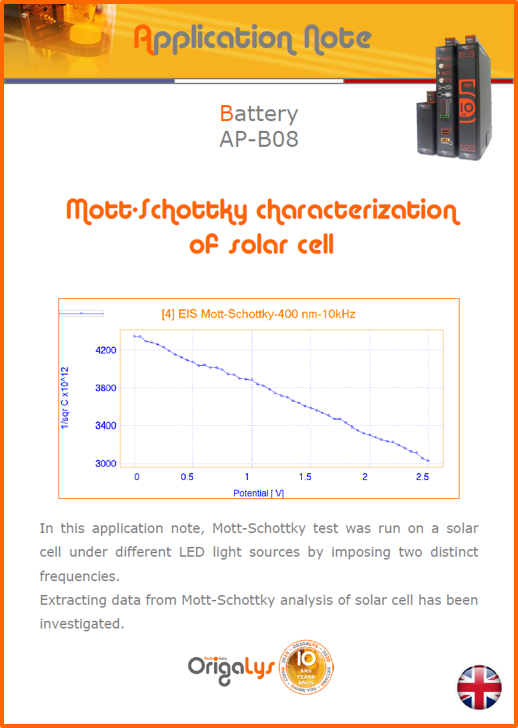
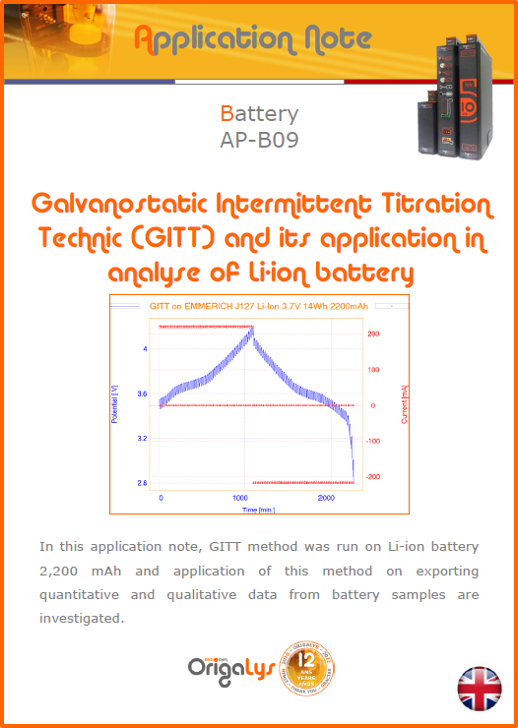
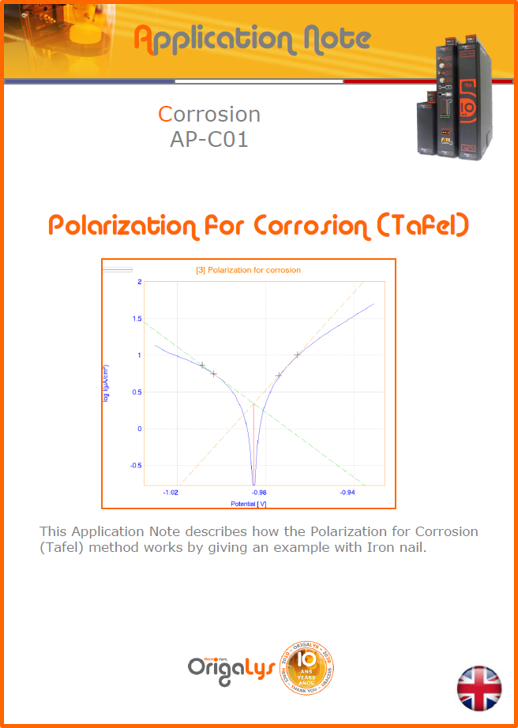
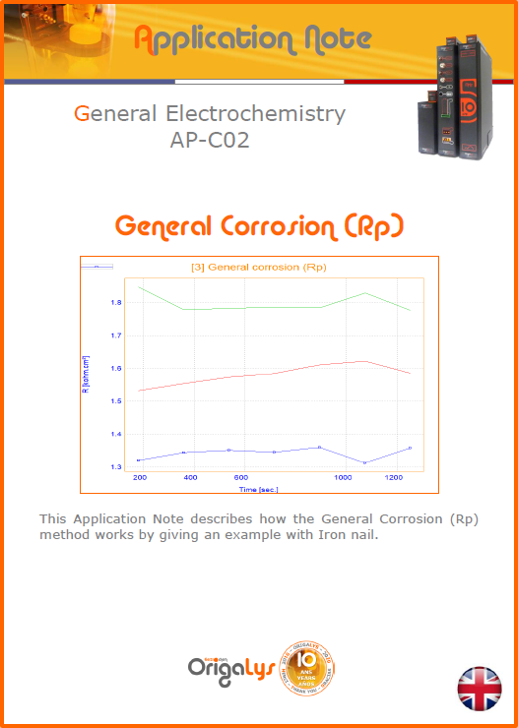
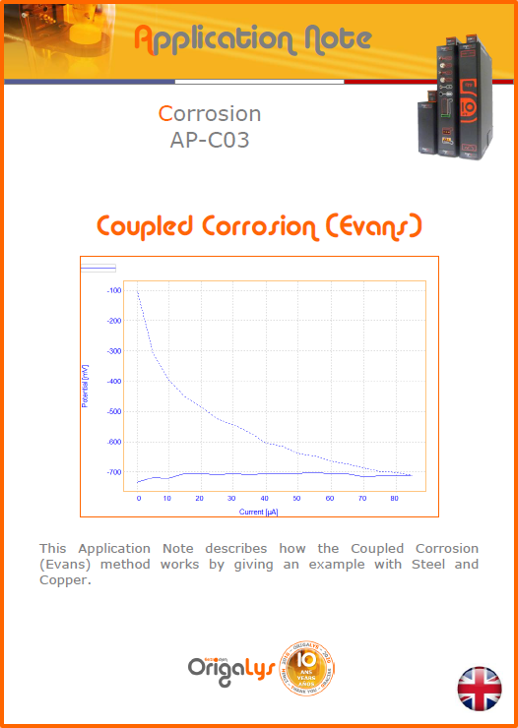
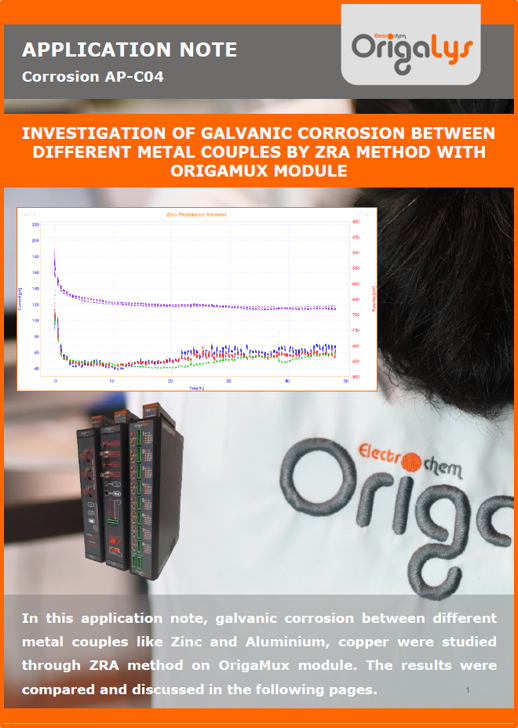
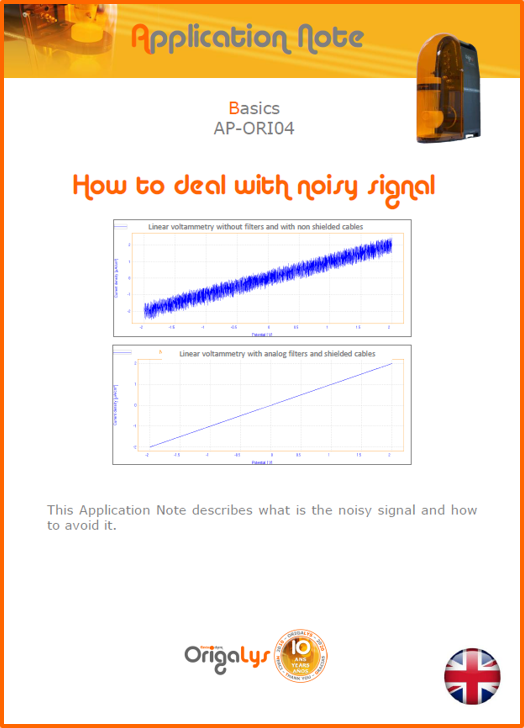
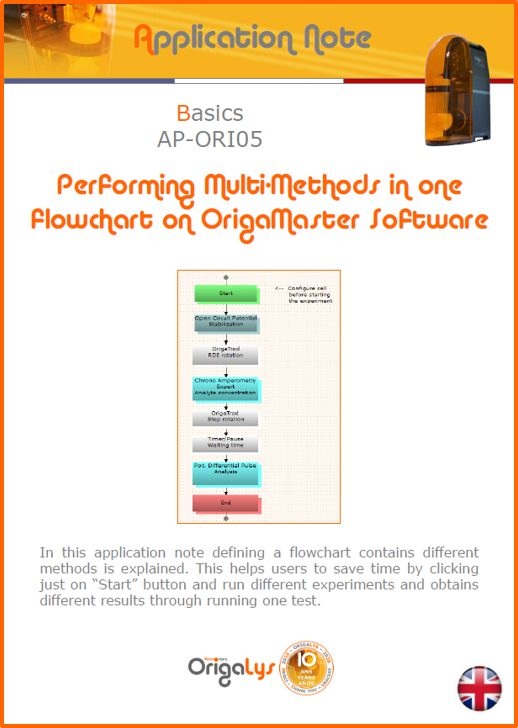
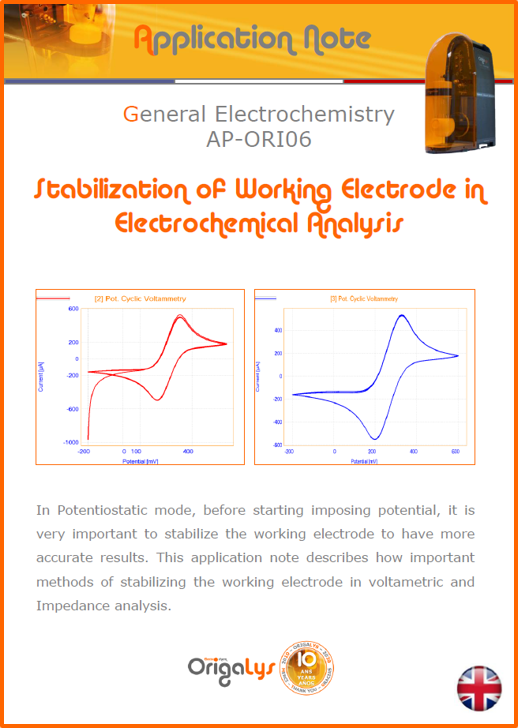
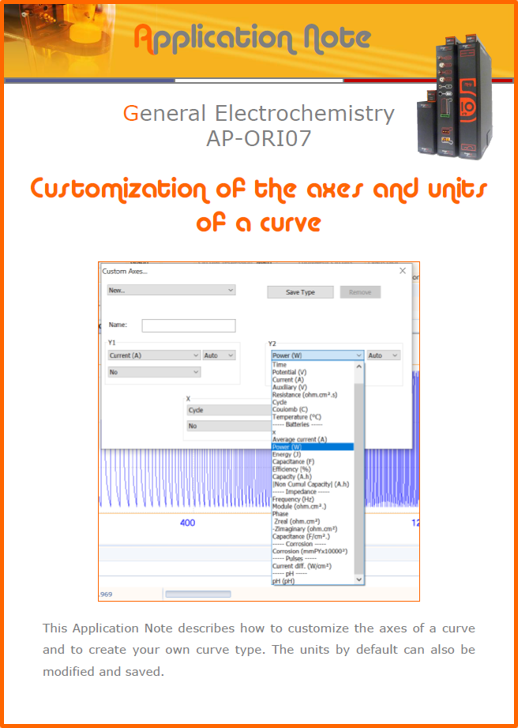
APPLICATION NOTESAre you looking for a particular application? Are you looking for a method explanation? Check out here all the application notes from OrigaLys team. General electrochemistry Battery Corrosion Basics Practical works Technical NOTEs Explanations about standard methods, such as CV, CA, CP, Staircase, Interactive and so on.Explanations about Battery methodsAP-B01 Expert Charge and Discharge CycleLearn how to use the Expert Charge and Discharge Cycle method, thanks to a standard battery: Ni-Cd 1.2 V, 600 mAh. AP-B02 Single Charge or DischargeLearn how to use the Expert Charge and Discharge Cycle method, thanks to a standard battery: Ni-Cd 1.2 V, 600 mAh. AP-B03 Constant PowerThis Application Note describes about a very useful method for testing batteries in long or short term. The power of battery will be kept constant by imposing current and measuring potential during time. Changing the potential and current of the battery, will be investigated. AP-B04 Photovoltaic - Solar CellThis Application Note describes how we can analyze behavior of solar cell with photovoltaic method and accessories : LED optical bench and OCP/Impedance methods. AP-B06 I-V CharacterisationThis Application Note describes how to analyze solar cells with IV Characterization method and LED light sources. AP-B07 OrigaDiff - Differential AmplifierThis Application Note describes how to use the OrigDiff to measure two additionnal voltages (REF3 & REF4) in a cell. AP-B08 Mott-Schottky on Solar cellThis Application Note describes a test made on solar cell with LED light source. Explanations about Corrosion methods, such as Tafel, Rp or EvansAP-C01 Polarization for Corrosion (Tafel)Learn how to use the Polarization for Corrosion method and Tafel post-treatment, thanks to a standard sample: Iron nail. AP-C02 General Corrosion (Rp)Learn how to use the General Corrosion method to get Rp value, thanks to a standard sample: Iron nail. AP-C03 Coupled Corrosion (Evans)Learn how to use the Coupled Corrosion method and perfom Evans post-treatment, thanks to a standard samples: Copper and Steel. Explanations about electrochemical vocabulary or some tips about the accessories or instrumentsAP-ORI02 How to check the electrode cablesLearn how to check your electrode cables to be sure it's fully operational. AP-ORI04 How to deal with noiseLearn how to understand what a noisy signal is and how to avoid it by easy tricks and also by software parameters. AP-ORI05 How to create multi-method sequenceLearn how to create different configuration of sequences: different methods, same methods with same parameters, manual loops, same methods with different parameters, and so on. AP-ORI06 Stabilization of Working Electrode in Electrochemical AnalysisIt is highly important to stabilize the working electrode to get the most accurate result possible. Learn how to do it in this application note. AP-ORI07 Axis customization, creation of curve typesWith "custom type" window, it is possible to customize the axes of a curve and so create your own profile of curve, your own "type" of curve. Learn how to do it with the application note. All our Practical works, made for Teaching purposeTP-0 Introduction to CorrosionLearn how Corrosion can be analyzed with potentiostat. We propose some experiments in order to be more familiar with corrosion tests: Pitting, Galvanic, General, Passivation, etc. TP-1 Study of the electrochemical inertia domain of the solventWith this Practical work, we explain how the students can trace the intensity-potential curve of water (i=f(E)). TP-2 Ferri/Ferrate Cyanide systemWith this Practical work, we explain how the students can trace the intensity-potential curve of Ferri/Ferrate Cyanide (i=f(E)). TP-3 Galvanic CorrosionWith this Practical work, we explain the principles of the Galvanic Corrosion. Then, we propose an example with Steel and Copper. TP-4 Pitting CorrosionWith this Practical work, we explain the principles of the Pitting Corrosion. Then, we propose an example with Stainless Steel. TP-5 Flade MethodWith this Practical work, we explain the principles of the Flade method. Then, we propose an example with Iron. Do you need more information? Contact us +33 9 54 17 56 03 or fill the form |